Release time: March 13, 2023
Views: 2321
Heat dissipation technology mainly refers to the methods, techniques, and approaches used in the external thermal design, involving various aspects related to heat transfer, cooling methods, materials, etc. Currently, almost all heat sinks rely on heat conduction and convective heat transfer as the primary means of dissipating heat. Depending on the different means of heat conduction and convective heat transfer, heat sink products can be categorized into two types: active and passive.
Active heat dissipation means that there is an unrelated energy source involved in the forced cooling process, such as fans, water pumps in liquid cooling, or compressors in phase-change cooling. These active cooling methods generally offer higher efficiency but require additional energy sources. On the other hand, passive heat dissipation relies solely on the natural convection of the heat source or heat sink to dissipate heat. Commonly used heat dissipation technologies include natural cooling, forced cooling, liquid cooling, and active cooling.
1. Natural Cooling:
Natural cooling is a commonly used heat dissipation method that utilizes materials (primarily heat-conductive materials) to absorb and dissipate heat into the surrounding air. This method is used when specific airflow requirements are not needed. Heat sink materials such as copper-aluminum composite sheets, aluminum extrusions, machined heat sinks, or heat-conductive alloy castings are employed to achieve heat dissipation in products. Natural cooling is typically used for electronic components with low temperature control requirements and relatively low heat flux density, especially in low-power devices and components.

2. Forced Cooling:
Forced cooling involves accelerating the airflow around electronic components using methods like fans to remove heat. Air-cooling is a widely used cooling technology that is relatively simple to manufacture, has lower costs, and is easy to install. It is suitable for electronic components that have sufficient space for airflow or when some cooling facilities are installed. Increasing the total heat dissipation area and generating a relatively higher convective heat transfer coefficient on the heat dissipation surface are key ways to enhance the effectiveness of forced cooling.
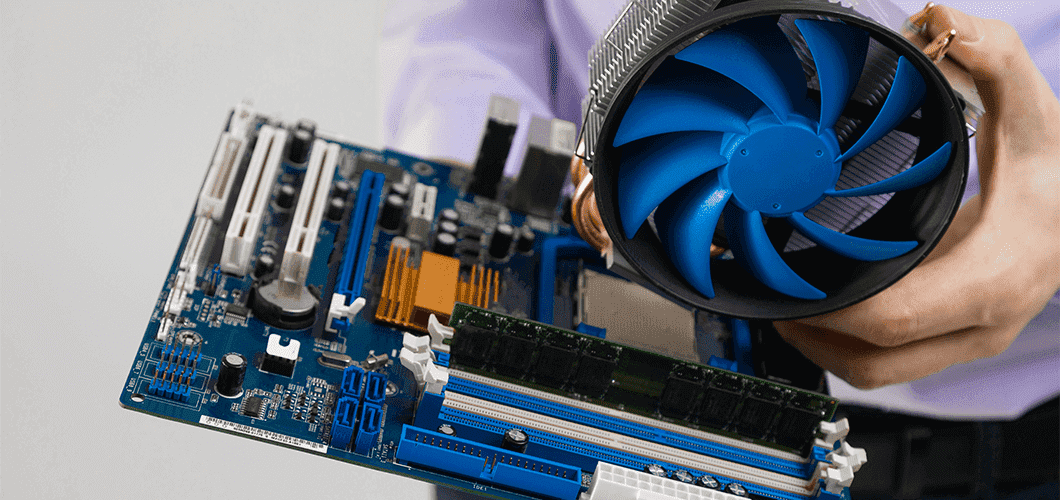
3. Liquid Cooling:
Liquid cooling is a heat dissipation method applied to electronic components based on chip and chip module cooling. It can be divided into direct and indirect liquid cooling. Indirect liquid cooling involves using a liquid coolant that comes into contact with the electronic components, and through an intermediate medium system, heat is transferred using liquid modules, heat-conductive modules, liquid jet modules, and liquid substrates. Direct liquid cooling, also known as immersion cooling, directly contacts the liquid with the relevant electronic components. The cooling liquid absorbs and removes heat, making it suitable for devices with relatively high heat dissipation density or those used in high-temperature environments.

4. Active Refrigeration Heat Dissipation:
Active refrigeration heat dissipation involves two main methods: phase-change cooling using refrigerants and semiconductor cooling.
a. Phase-change cooling using refrigerants: Deep cooling technology is valuable and impactful for electronic component cooling. It can be applied to computer systems with relatively high power where it enhances circulation efficiency and offers a wide range of cooling quantities and temperature ranges. The overall equipment structure becomes more compact, and circulation efficiency is relatively high.
b. Semiconductor cooling: Semiconductor cooling, also known as thermoelectric cooling, is a method used to dissipate or cool conventional electronic components. It offers advantages like compact size, easy installation, good quality, and easy disassembly. This method utilizes the Peltier effect of semiconductor materials. By passing direct current through different semiconductor materials in series, a thermocouple is formed. This allows heat absorption and release at both ends of the thermocouple, achieving a cooling effect.
Looking for more
information?

0755 23405284
Email: sale02@hj-tc.com
Add: 3/F No.5 Building,Yesun Pingshan Life and Health Technology Park, No. 19 Linhui Road,Pingshan District, Shenzhen, Guangdong,CN.
©2019- 2024 Huajing Co.,Ltd.Copyright